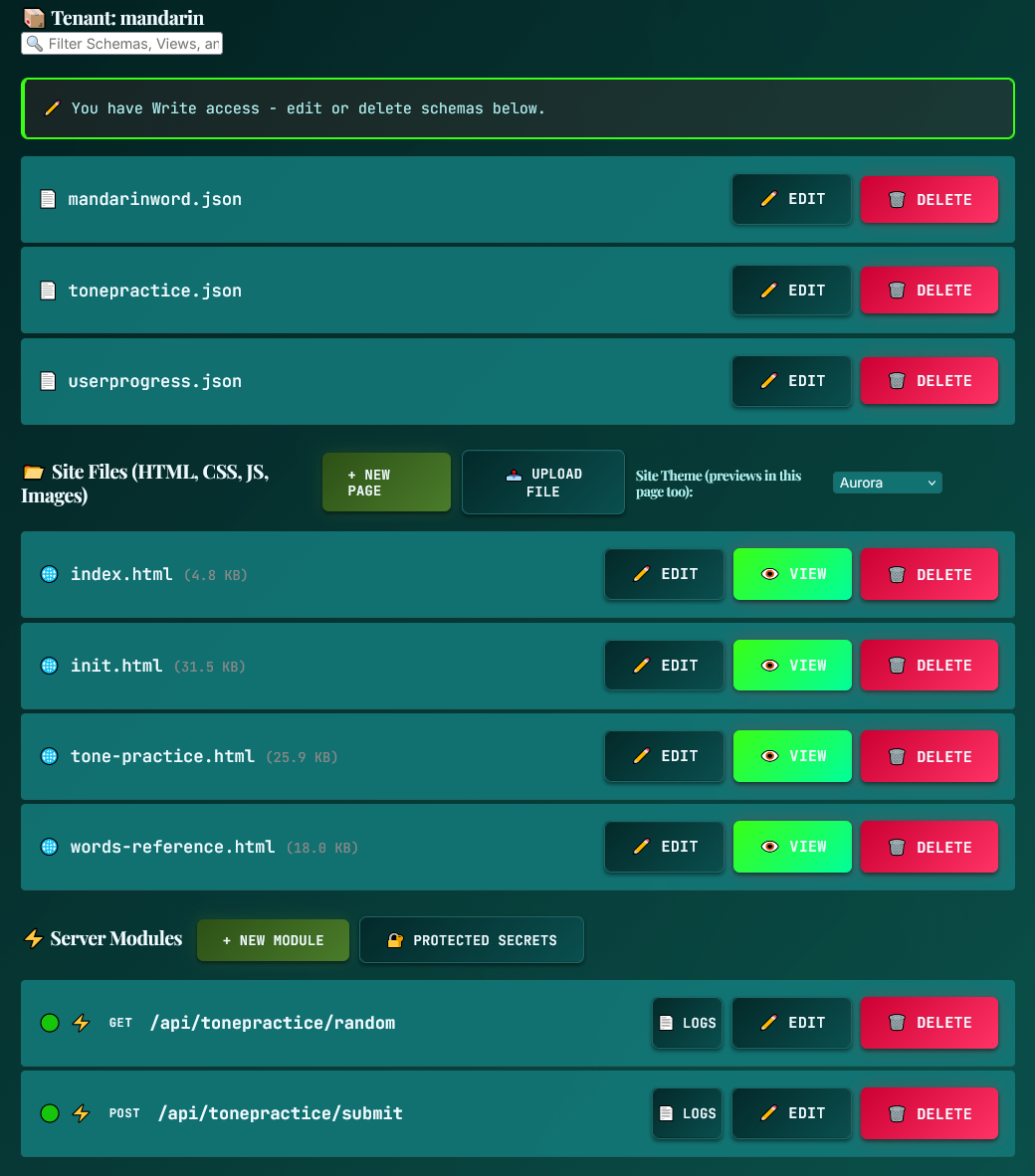
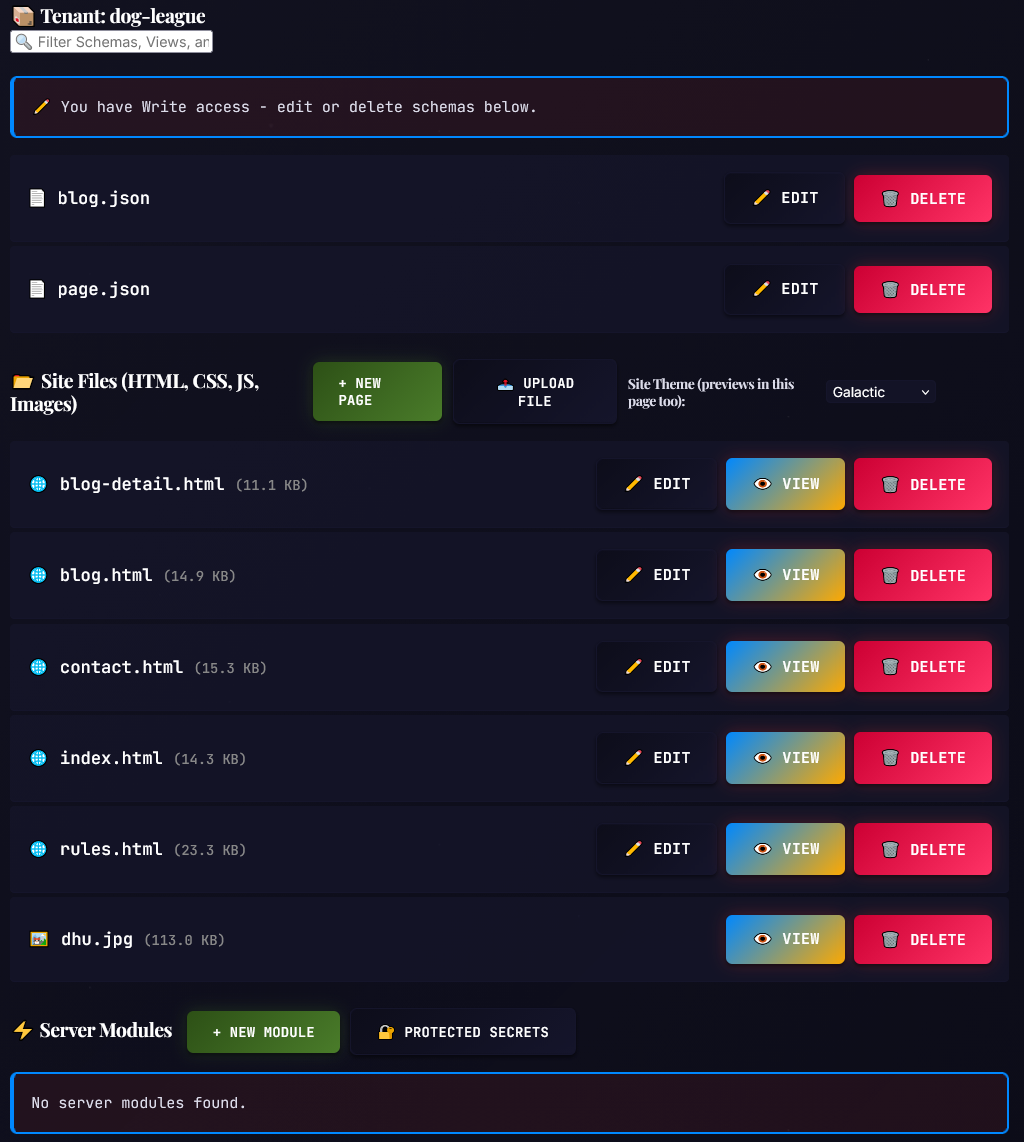
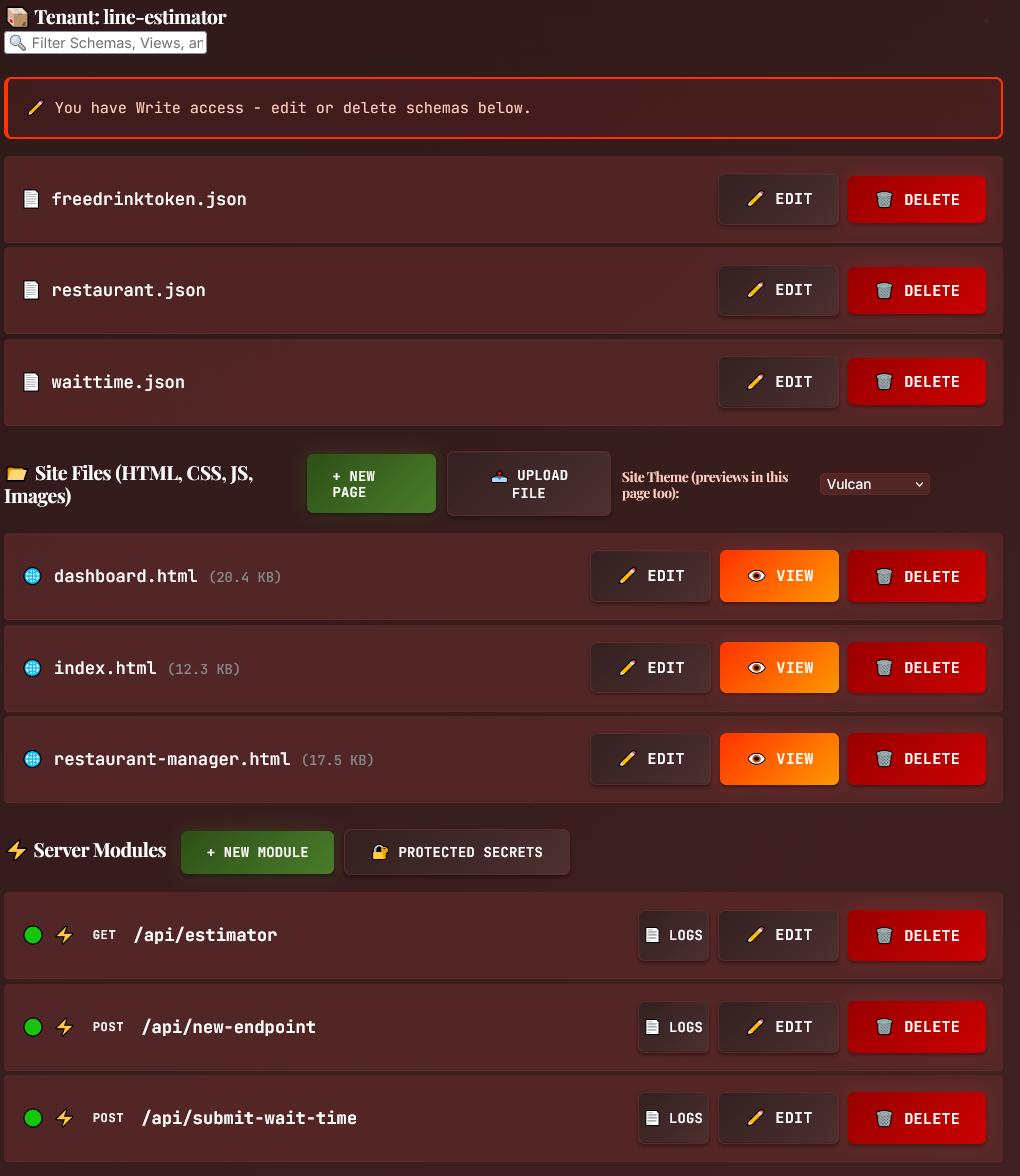
Workflows & Architecture
Blockforger supports multiple architectural patterns depending on your needs. Choose the workflow that best fits your use case. You can always switch your workflow later: the schemas are what enables all of them.
Frontend-Only: Import as API Client
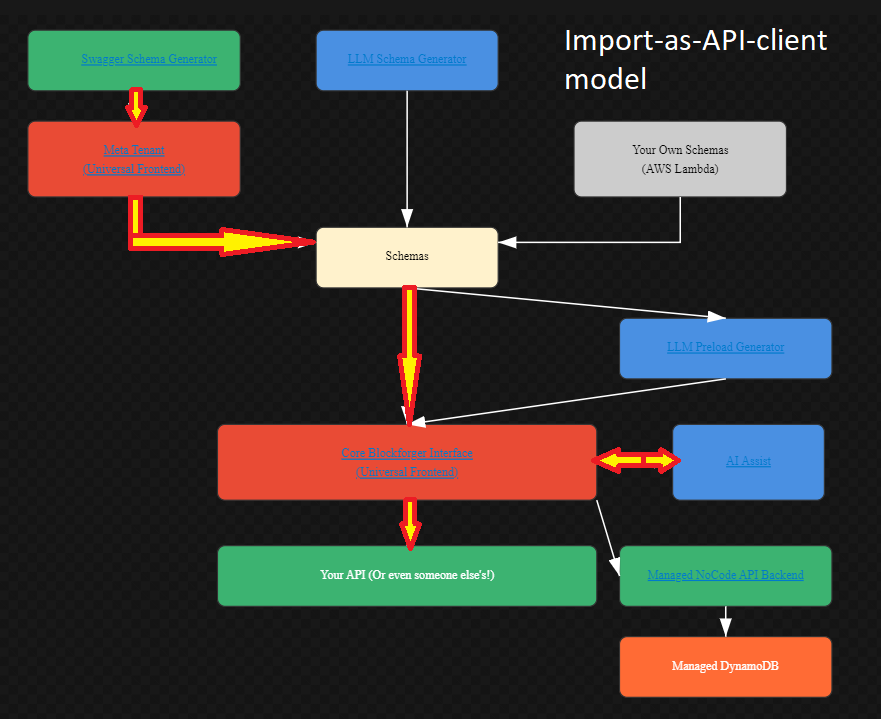
This workflow is ideal when you already have an existing API and want to build a visual control panel for it.
How It Works:
- Schema Generation:
- Use the Swagger Schema Generator to import your existing API specification
- Use the Postman Collection Import to instantly convert Postman collections
- Or use the LLM Schema Generator to create schemas from descriptions
- Or upload Your Own Schemas directly
- Schema Management:
- All schemas are managed through the Meta Tenant (universal frontend)
- Schemas are stored centrally and made available to the core interface
- Universal Frontend:
- The Core Blockforger Interface uses your schemas to generate a drag-and-drop control panel
- AI Assist provides real-time help and transformations
- LLM Preload Generator can pre-fill forms with sample data
- API Integration:
- The frontend connects directly to Your API (or any external API)
- No backend hosting required - you manage your own API
- Perfect for integrating with existing systems
Use Cases:
- Building admin panels for existing APIs
- Creating visual interfaces for third-party APIs
- Prototyping API interactions without backend changes
- Data entry interfaces for external services
Full-Stack: Instant Backend
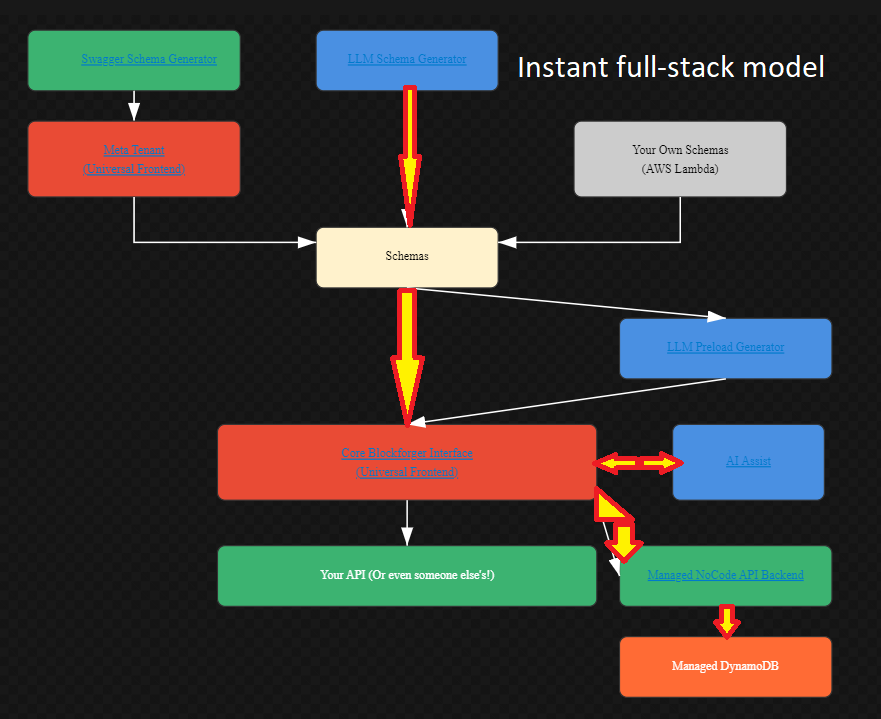
This workflow provides a complete full-stack solution with managed backend hosting and database storage.
How It Works:
- Schema Generation:
- Generate schemas using Swagger, LLM, or upload your own
- Schemas flow through the Meta Tenant for management
- All schemas are centralized for the core interface
- Universal Frontend:
- The Core Blockforger Interface provides the visual control panel
- AI Assist offers interactive AI-powered assistance
- LLM Preload Generator creates sample data automatically
- Managed Backend:
- Enable Managed NoCode API Backend in tenant settings
- Automatic REST API generation (POST, GET, PUT, PATCH, DELETE)
- Built-in authorization and validation
- No code required - fully managed by Blockforger
- Database Storage:
- Data is automatically stored in Managed DynamoDB
- Configure capacity modes (on-demand, provisioned, or auto-scaling)
- Automatic indexing and query optimization
Use Cases:
- Rapid prototyping of new applications (because who has time to write boilerplate?)
- Building MVPs without backend development (your product manager will love you)
- Internal tools and admin panels (finally, a tool that doesn't look like it was designed in 1995)
- Applications that need simple CRUD operations (the bread and butter of most apps)
dynamo_backend: "true" in your
tenant's backendoptions. See AWS Integrations for
configuration details. It's literally one flag to get started. We told you we like to keep things
simple.
Hybrid: Backend as Document Manager
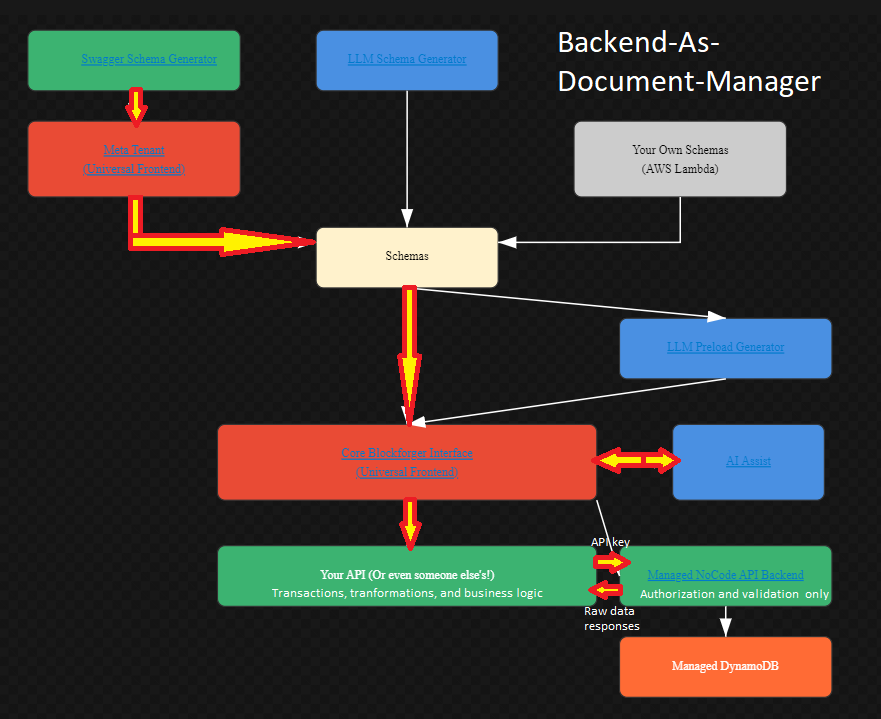
This workflow combines the managed backend with your own business logic layer, enabled by EventBridge's asynchronous I/O capabilities.
How It Works:
- Schema Generation:
- Generate schemas using Swagger, LLM, or upload your own
- Manage schemas through the Meta Tenant
- Schemas are centralized for the universal frontend
- Universal Frontend:
- The Core Blockforger Interface provides the visual control panel
- AI Assist offers real-time transformations and help
- LLM Preload Generator creates sample data
- Your Business Logic Layer:
- Implement your own API with custom business logic
- Handle complex operations: aggregations, joins, transformations, transactions
- Manage workflows, validations, and business rules
- Can be hosted anywhere (AWS Lambda, your own servers, etc.)
- Managed Backend (Document Manager):
- The Managed NoCode API Backend acts as a persistence layer
- Handles authorization and validation only
- Stores data in Managed DynamoDB
- Provides simple CRUD operations
- EventBridge Integration (Key Feature):
- EventBridge provides asynchronous I/O between your API and the managed backend
- Instead of waiting for synchronous API responses, events are published asynchronously
- Your API can process events in the background
- Enables complex workflows without blocking the frontend
The Hybrid Flow:
The hybrid model uses EventBridge for asynchronous I/O, allowing your API to implement complex business logic while the managed backend handles persistence:
- Frontend → Your API: The universal frontend sends requests to your custom API
- Your API → EventBridge (input): Your API performs additional business logic and publishes events to the persistence layer via EventBridge
- EventBridge (input) → Managed No-code Backend: Events are received by the managed backend, which performs authorization and validation, then persists data to DynamoDB
- Managed No-code Backend → EventBridge (output): The managed backend publishes events containing the results of what the persistence layer actually completed
- EventBridge (output) → Your API: Your API receives events asynchronously for any additional metrics, state maintenance, and processing to reflect successful persistence changes
- Your API → Frontend: Your API can respond immediately (fire-and-forget) or wait for confirmation events
Benefits of Asynchronous I/O:
- Non-Blocking Operations: Don't wait for database writes - process them asynchronously
- Complex Workflows: Handle multi-step processes, aggregations, and joins without blocking
- Better Performance: Frontend gets immediate responses while backend processes in background
- Scalability: Event-driven architecture scales better for high-volume operations
- Flexibility: Implement complex business logic without modifying the managed backend
Example Use Cases:
- E-commerce: Process orders, update inventory, send notifications asynchronously
- Data Aggregation: Collect data from multiple sources, aggregate, then store
- Workflow Management: Multi-step approval processes with async notifications
- Analytics: Collect events, process analytics, update dashboards asynchronously
- Integration Hub: Connect multiple systems with complex transformation logic
Configuration:
To enable the hybrid workflow:
- Enable
dynamo_backend: "true"in your tenant'sbackendoptions - Configure
eventbridge-outputto publish events from the managed backend - Configure
eventbridge-input: "true"to receive events in your API - Set up EventBridge rules to route events to your API (Lambda, SQS, etc.)
- Create API keys for your custom API to authenticate with the managed backend